Double spending is the digital nightmare that haunts every crypto transaction. Most people assume blockchain math makes stealing the same Bitcoin twice impossible, but that belief is shakier than it seems. Researchers found that certain crypto networks are more than twice as likely to fall victim to double spending attacks compared to others. This hidden flaw raises urgent questions about the real security of your coins.
Double spending represents a critical vulnerability in digital currency systems where a malicious actor attempts to use the same digital token multiple times. This fundamental problem threatens the core integrity of cryptocurrency transactions and challenges the fundamental trust mechanisms that make digital currencies viable.
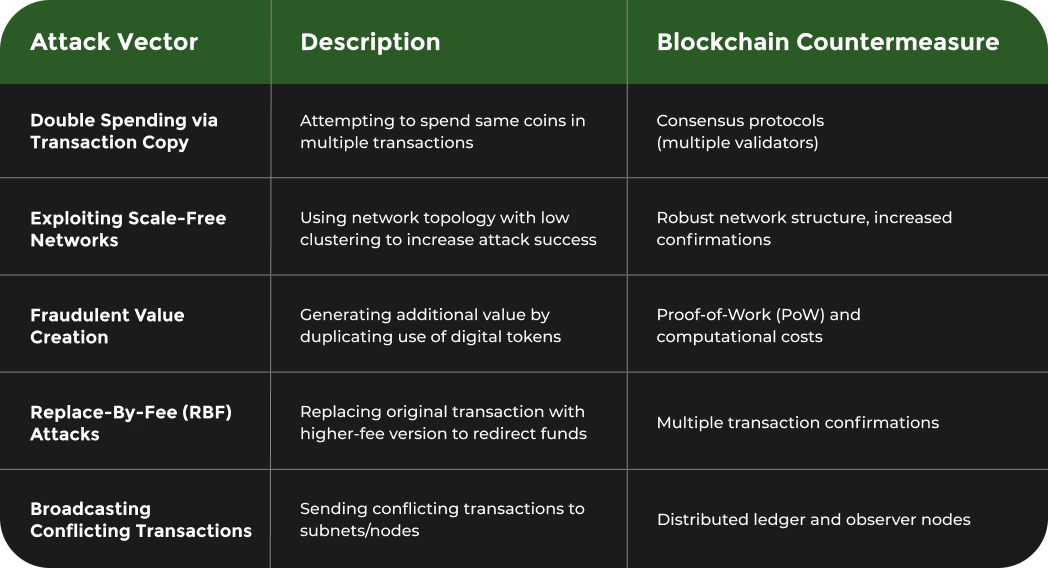
In a typical double spending scenario, a bad actor tries to spend the same cryptocurrency units in multiple transactions simultaneously, effectively creating fraudulent value out of thin air. Research from the International Journal of Blockchain Studies reveals that certain network characteristics significantly impact the vulnerability to such attacks. Surprisingly, the study found that network topology plays a crucial role in determining susceptibility to double spending.
Specifically, scale-free networks like many cryptocurrency platforms demonstrate a higher probability of successful double spending attempts. The research indicates that these networks are more than twice as likely to experience double spending compared to more structured network configurations. This vulnerability stems from the network’s low clustering coefficient, which makes it easier for malicious actors to exploit transaction verification processes.
Blockchain technology introduces several sophisticated countermeasures to prevent double spending. Researchers from the Cryptography and Security Research Center have identified multiple strategies blockchain platforms use to mitigate these risks. The primary defense mechanism is the consensus protocol, which requires multiple network participants to validate and confirm transactions before they are permanently recorded.
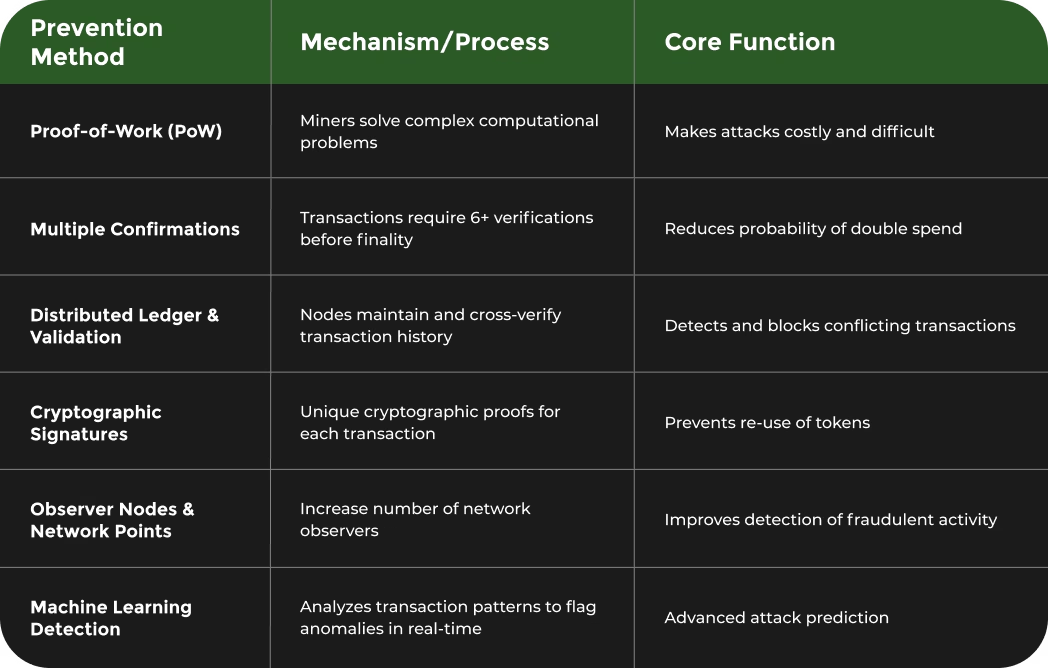
Proof-of-Work (PoW) stands out as a fundamental strategy originally proposed by Satoshi Nakamoto in the Bitcoin whitepaper. This mechanism requires computational work to validate transactions, making it economically prohibitive for attackers to manipulate the blockchain. Miners must solve complex mathematical problems, which creates a significant barrier against double spending attempts.
The implications of double spending extend far beyond theoretical concerns. When successful, these attacks can undermine the entire economic foundation of a cryptocurrency by eroding user trust and creating artificial inflation. Each successful double spend represents a direct theft of value, potentially destabilizing entire digital currency ecosystems.
Understanding double spending is not just a technical exercise but a critical component of cryptocurrency security. As digital currencies continue to evolve, the ongoing battle against these sophisticated attacks remains a top priority for blockchain developers and security experts worldwide. The complexity of preventing double spending highlights the sophisticated nature of cryptocurrency infrastructure and the continuous innovation required to maintain its integrity.
To help clarify the mechanics of double spending and blockchain’s main defense strategies, the table below summarizes key attack vectors and the corresponding blockchain countermeasures mentioned in the article.
Double spending poses a profound existential threat to Bitcoin and broader cryptocurrency markets, potentially undermining the fundamental trust mechanisms that make digital currencies viable. The economic implications of successful double spending attacks extend far beyond mere technical vulnerabilities, representing a systemic risk to the entire blockchain ecosystem.
The potential for double spending creates significant market uncertainty. Research from ACM Digital Library demonstrates that without appropriate detection techniques, double spending attacks can succeed with overwhelming probability and can be mounted at remarkably low cost. This finding suggests that even small-scale malicious actors could potentially inflict substantial economic damage.
When double spending occurs, the immediate consequences ripple through cryptocurrency markets. Investors lose confidence, exchange platforms become hesitant to process transactions, and the perceived reliability of the blockchain infrastructure diminishes. The attack essentially creates artificial currency inflation, diluting the value of legitimate holdings and eroding the economic foundation that supports cryptocurrency valuations.
Innovative research from computer science experts has developed advanced detection models that can predict double spending attempts with up to 95% accuracy. These sophisticated techniques involve analyzing transaction memory pools across network nodes, creating a robust defense mechanism against potential attacks.
One critical strategy involves increasing the number of network observer nodes, which significantly enhances the ability to detect and prevent fraudulent transactions. By creating multiple verification points, blockchain networks can create increasingly complex barriers that make double spending economically unfeasible.
The market implications extend beyond immediate financial losses. A single successful double spending attack can trigger widespread panic, potentially causing massive selloffs and long-term reputational damage to specific cryptocurrencies. Learn more about blockchain security strategies to understand how these risks are being systematically addressed.
Moreover, recent studies on Bitcoin payment systems highlight that Replace-By-Fee attacks represent the most significant threat to transaction integrity. These sophisticated attack vectors demonstrate the continuous arms race between blockchain developers and potential malicious actors.
As cryptocurrency markets mature, the ability to prevent and detect double spending becomes increasingly crucial. The ongoing development of more sophisticated consensus mechanisms, enhanced verification protocols, and advanced machine learning detection models represents a critical frontier in maintaining the integrity of digital financial systems.
Ultimately, the threat of double spending underscores the complex technological and economic challenges inherent in decentralized financial technologies. Each advancement in prevention techniques represents not just a technical achievement, but a critical step toward establishing cryptocurrencies as a reliable, trustworthy alternative to traditional financial infrastructure.
Preventing double spending represents a critical challenge in Bitcoin mining, requiring sophisticated technological strategies that protect the integrity of digital transactions. The fundamental goal is to create an immutable, transparent system that makes fraudulent attempts economically unfeasible and technically complex.
According to the original Bitcoin whitepaper by Satoshi Nakamoto, the primary defense against double spending involves a peer-to-peer distributed timestamp server that generates computational proof of transaction chronological order. This mechanism fundamentally relies on proof-of-work as the core security protocol.
The proof-of-work system requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems, which creates significant computational barriers against potential double spending attacks. Each solved block becomes part of a cryptographically secured chain, making retroactive modifications extremely difficult. Miners must invest substantial computational resources, which economically disincentivizes malicious behavior.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology emphasizes the critical role of network-wide consensus in preventing double spending. Bitcoin implements a multi-layered verification process where transactions require multiple confirmations before being considered irreversible. Typically, merchants and exchanges wait for six confirmations, which mathematically reduces the probability of a successful double spend to near zero.
Each subsequent block added to the blockchain makes previous transactions increasingly secure. The computational work required to alter historical transactions grows exponentially, creating a robust deterrent against potential attackers. This exponential difficulty ensures that attempting to rewrite transaction history becomes economically impractical.
The following table summarizes the main blockchain prevention methods for double spending as described in the article, detailing mechanisms and their core functions.
Modern Bitcoin mining infrastructure has developed sophisticated techniques to detect potential double spending attempts in real-time. Machine learning algorithms now analyze transaction patterns, identifying suspicious activities with increasing accuracy. Learn more about advanced blockchain security strategies to understand the cutting-edge approaches being developed.
Network nodes play a crucial role in this prevention strategy. By maintaining a distributed ledger where multiple independent participants verify transactions, the system creates multiple layers of validation. If a malicious actor attempts to broadcast conflicting transactions, the network can quickly identify and reject these attempts.
Cryptographic signatures and unique transaction identifiers further complicate double spending attempts. Each transaction contains cryptographic proof that can be verified independently, ensuring that the same cryptocurrency units cannot be spent multiple times without detection.
The ongoing evolution of prevention methods demonstrates the dynamic nature of blockchain security. As computational technologies advance, so do the strategies for protecting digital currency ecosystems. Bitcoin mining continues to represent a frontier of technological innovation, where complex mathematical protocols serve as the guardians of financial integrity in the digital age.
Ultimately, preventing double spending is not just a technical challenge but a continuous arms race between potential attackers and blockchain developers. Each advancement represents a step toward creating more robust, trustworthy digital financial systems that can withstand increasingly sophisticated technological threats.
Double spending represents a profound risk that fundamentally challenges the economic stability and trust mechanisms for both cryptocurrency investors and miners. The potential for fraudulent transactions creates a complex landscape of financial uncertainty that extends far beyond simple technological vulnerabilities.
Recent blockchain security research highlights the critical implications of double spending for crypto asset credibility. Investors face substantial risks, including potential transaction reversals and unexpected capital losses. When double spending occurs, the immediate market reaction can trigger massive sell-offs, causing rapid value depreciation and eroding investor confidence.

The financial exposure is particularly acute for institutional and retail investors who rely on the immutability of blockchain transactions. A single successful double spending attack can create cascading economic consequences, potentially wiping out significant portfolio values. This risk premium forces investors to implement more sophisticated due diligence processes and risk management strategies when engaging with cryptocurrencies.
For cryptocurrency miners, double spending threats directly impact the economic incentives underlying proof-of-work networks. Miners invest substantial computational resources in maintaining network integrity, and any vulnerability that undermines this system threatens their fundamental business model. The potential for double spending attacks creates an environment of uncertainty that can discourage mining participation and reduce overall network security.
The economic calculations for mining profitability become increasingly complex when considering potential double spending risks. Miners must continuously invest in advanced detection technologies and participate in robust consensus mechanisms to mitigate these threats. Learn more about mining security strategies to understand the evolving landscape of blockchain protection.
Moreover, repeated double spending attempts can lead to reduced trust in specific cryptocurrencies, potentially driving away both investors and miners. The reputational damage extends beyond immediate financial losses, creating long-term challenges for ecosystem growth and adoption.
The intricate relationship between investors and miners creates a unique ecosystem where technological security directly translates to economic stability. Each prevention mechanism represents not just a technical safeguard but a critical economic defense that protects the interests of all network participants.
As cryptocurrency markets mature, the ability to effectively prevent and respond to double spending attempts becomes a key differentiator for blockchain platforms. Investors and miners alike are increasingly demanding more sophisticated, transparent, and secure transaction verification processes that can withstand increasingly complex technological threats.
Ultimately, the battle against double spending is more than a technical challenge. It represents a critical frontier in establishing cryptocurrencies as a reliable, trustworthy alternative to traditional financial systems. The ongoing innovation in prevention techniques demonstrates the resilience and adaptability of blockchain technologies in addressing fundamental economic vulnerabilities.
Double spending is a digital currency vulnerability where a malicious actor attempts to use the same cryptocurrency units in multiple transactions, threatening the integrity of the currency’s value.
Double spending attacks can occur when a bad actor tries to spend the same coins in several simultaneous transactions, often exploiting weaknesses in the network’s topology or transaction validation processes.
Preventative methods include consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Work, multiple transaction confirmations, cryptographic signatures, and advanced detection techniques utilizing machine learning to identify potential fraudulent activities.
Double spending poses a significant risk as it can lead to market volatility, loss of investor confidence, and potential economic damage, ultimately undermining the stability and trust in cryptocurrency networks.
Understanding the real risk of double spending can be overwhelming. You want to keep your Bitcoin investments safe, but complex attack vectors and the need for stronger network confirmations can make mining feel unpredictable. As highlighted in this article, weak network security and the growing sophistication of double spending attacks threaten not just your profits but also your trust in digital assets.

Take control with Blockware Solutions. Our Mining-as-a-Service empowers you to mine Bitcoin using professional-grade hosted hardware and access advanced research tools that address blockchain vulnerabilities. Rely on built-in security protocols and ongoing technical support to strengthen transaction integrity and minimize double spending risk. Visit Blockware Solutions today and start protecting your mining future with proven, expert-backed solutions.